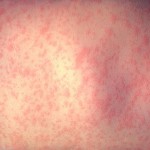
Childhood eczema, sometimes called atopic or infantile eczema, is a fairly common hereditary condition, which affects one in every eight babies. The skin becomes irritated and inflamed. It feels very itchy, and the child instinctively scratches, which aggravates the condition and can lead to the skin becoming broken and raw, and even in severe cases to infection.
At what age does childhood eczema occur?
Babies often tend to have dry skin soon after birth. This usually settles down naturally after the first few months of life. Childhood eczema generally first appears between the ages of 6 months and 2 years.
Keeping eczema under control
Emollients are the treatment of choice and should form the basis of regular daily treatment. Application of emollients reduces roughness and scaling, the itching and irritation are also relieved.
How to stop a child scratching?
The scratching associated with eczema is particularly hard for babies and children to resist, as the itch can be unbearable for them. Scratching often leads to the skin becoming sore and inflamed, eventually cracking and bleeding and may become infected. An effective way to stop a baby scratching is to use cotton mittens, both during the day and at night. Fingernails should be kept short and clean to avoid infection. Liberal use of emollients and the use of bath emollients is the best way to rehydrate and moisturise the skin.
John Duffy MPSI, Claregalway Pharmacy
Tel: 799 754
Open 9am–8pm Monday–Friday and 9am–6.30pm on Saturday.